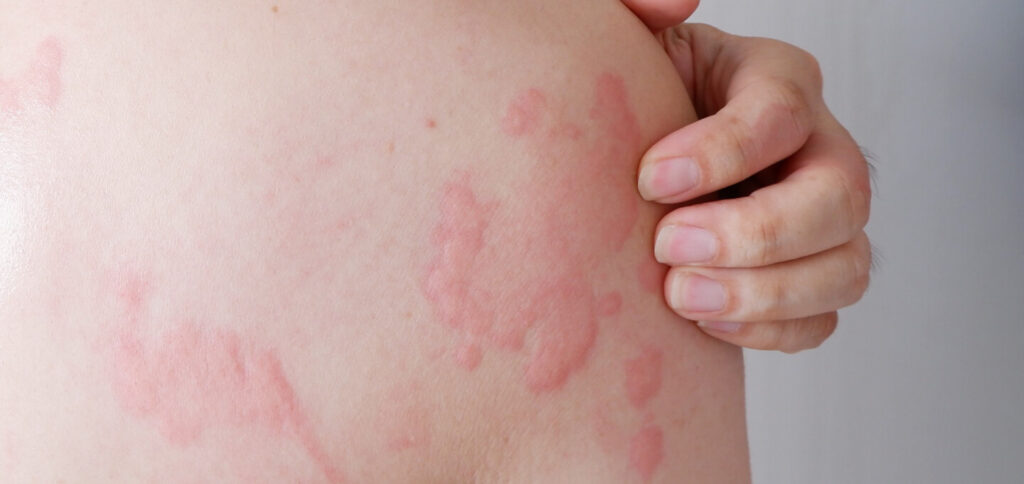
Hives, also known as urticaria, are a common skin condition that causes red, raised, itchy bumps on the skin. They can appear anywhere on the body and can range in size from small to large. Hives are usually harmless and go away on their own within a few hours or days. However, in some cases, they can be more severe and last for weeks or months.
What Are Hives?
Hives are caused by a release of histamines from the body’s mast cells. Histamines are chemicals that cause inflammation and itching. Hives can be triggered by a variety of things, including:
- Allergies: Hives are the most common allergic reaction. They can be triggered by food allergies, medication allergies, insect bites, or environmental allergies, such as pollen or pet dander.
- Infections: Hives can be a symptom of an infection, such as a cold, the flu, or a bacterial infection of the skin.
- Medications: Some medications, such as antibiotics, blood pressure medications, and pain relievers, can cause hives.
- Stress: Stress can trigger hives in some people.
- Physical factors: Hives can be triggered by physical factors, such as heat, cold, sunlight, or pressure.
Why Are Hives Common During Summer?
There are a few reasons why hives are more common during the summer. First, the warmer weather can trigger hives in some people. Second, people are more likely to be exposed to allergens during the summer, such as pollen and insect bites. Third, people are more likely to sweat during the summer, which can irritate the skin and trigger hives.
Allergies to Fish
Fish allergies are relatively rare, but they can cause hives. Fish allergies can be caused by any type of fish, but they are most common in people who are allergic to shellfish. Fish allergies can also cause other symptoms, such as swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, and nausea.
Do You Know Hives Can Appear Anywhere on the Body?
Yes, hives can appear anywhere on the body. However, they are most common on the arms, legs, torso, and face. Hives can also appear in the mouth, on the genitals, and in the eyes.
Treatment for Hives
Most cases of hives go away on their own within a few hours or days. However, there are a few things you can do to relieve the symptoms of hives, such as:
- Take an over-the-counter antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or loratadine (Claritin).
- Apply a cool compress to the affected area.
- Avoid scratching the hives, as this can make them worse.
- Take a warm bath or shower.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
If your hives are severe or do not go away after a few days, you should see a licensed independent practitioner. Your licensed independent practitioner may prescribe a stronger antihistamine or a steroid medication.
Prevention of Hives
There is no sure way to prevent hives, but there are a few things you can do to reduce your risk, such as:
- Avoid known allergens.
- Take steps to reduce stress.
- Stay cool during the summer.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing.
- Avoid scratching the hives.
If you have a history of hives, it is important to see a licensed independent practitioner if you develop any new symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat. These symptoms could be a sign of a more serious allergic reaction.